A. Kovács, B. Nyerges, V. Izvekov
Vibrational
analysis of
N-acetyl-α-d-glucosamine and
β-d-glucuronic acid
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 112 (2008) 5728-5735
The IR spectra of the solid and aqueous solutions of N-acetyl-a-d-glucosamine and b-d-glucuronic acid have been investigated by means of FT-IR spectroscopy and quantum chemical DFT calculations. The errors of the computed harmonic force field were corrected according to the scaled quantum mechanical (SQM) method of Pulay using partly literature, partly here developed scale factors. The scale factors for the hydrogen-bonded OH groups were determined by an SQM treatment of ethylene glycol. The IR spectra and test computations revealed that b-d-glucuronic acid is present as dimer, formed by hydrogen bonding between the COOH groups, in the solid phase. Based on the calculated results, 64 and 56 bands in the 4000-50 cm-1 range of the FT-IR spectra have been assigned for N-acetyl-a-d-glucosamine and b-d-glucuronic acid, respectively.
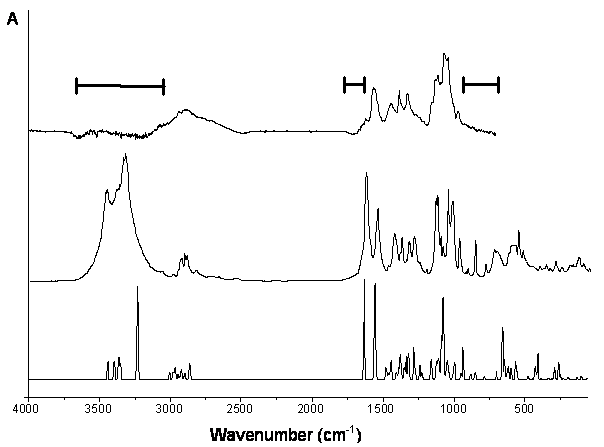
Experimental (top: aqueous solution; middle: solid) and computed (bottom) IR spectra of N-acetyl-a-d-glucosamine.
The marked ranges in the spectrum of aqueous solution indicate strong solvent absorptions.
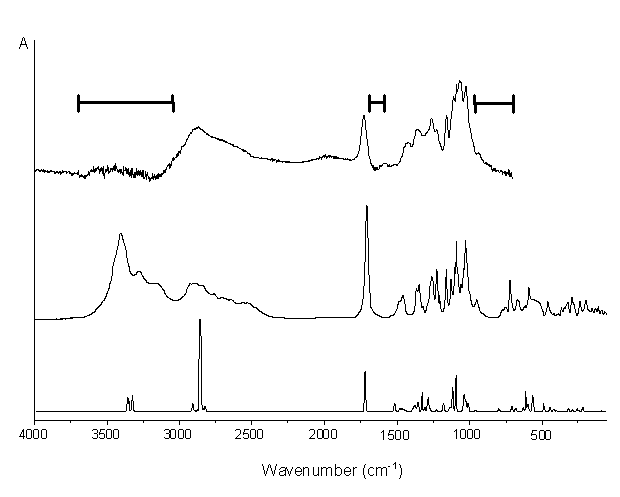
Experimental (top: aqueous solution; middle: solid) and computed (bottom) IR spectra of b-d-glucuronic acid.
The marked ranges in the spectrum of aqueous solution indicate strong solvent absorptions.
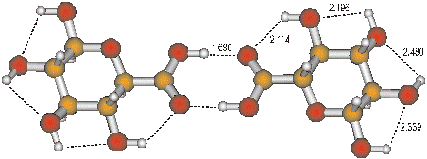
The computed structure of the b-d-glucuronic acid dimer hydrogen-bonded through the COOH groups.
The hydrogen bond length (dashed lines) are given in angstroms.
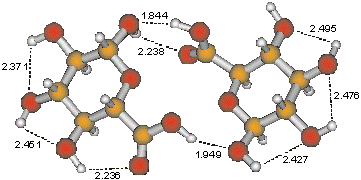
The computed dimer of b-d-glucuronic acid connected by hydrogen bonds between COOH and OH groups.